Employees Relations, Recruitment, Learning & Development, Payroll, etc.
Introduction: Human Resource Management (HRM) is the strategic and coherent approach to managing an organization’s most valuable asset – its people.
HR ensures success by recruiting, developing, and supporting employees effectively.
Key responsibilities include recruitment, training, performance management, compensation, employee relations, policy development, admin, and strategic planning.

Evolution of HR Over Time
Phase 1 (1900–1940): Administrative Roots
HR began as “personnel management”, focusing on pay, discipline, and attendance. The first known department started in NCR in 1901 post a labor strike.
Building the Foundation: The Early Days of Human Resources Management and the Legacy of John H. Patterson
The origins of modern HR trace back to the National Cash Register Company (NCR), where in 1901, following a significant employee strike, John H. Patterson established the first dedicated HR department.
The strike exposed the need for structured employee care and organizational responsiveness.
Patterson responded by introducing fair wages, profit-sharing, and the eight-hour workday, which greatly enhanced morale and reduced turnover.
He launched NCR’s first employee training program and formalized personnel recordkeeping, and implemented a suggestion system to hear employee feedback.
These practices moved HR from mere clerical administration to a strategic and humane discipline, setting the foundation for modern HR.
Source Michael Burgus – LinkedIn
Phase 2 (1940–1970): Legal Impact
The rise of civil rights, safety regulations, and equal employment laws forced HR to adopt compliance and employee protection roles.
Phase 3 (1980–2000): Specialization and Strategic Role
HR evolved into a strategic function. Ulrich’s model introduced HR Business Partners, centers of excellence, and shared services.
Dave Ulrich’s HR Model
Background:
In 1997, Professor Dave Ulrich, a leading HR thinker, published “Human Resource Champions”, proposing a bold shift: HR must go beyond administration and become a strategic partner in driving business success.
His model became a global standard, redefining how HR adds value to organizations.
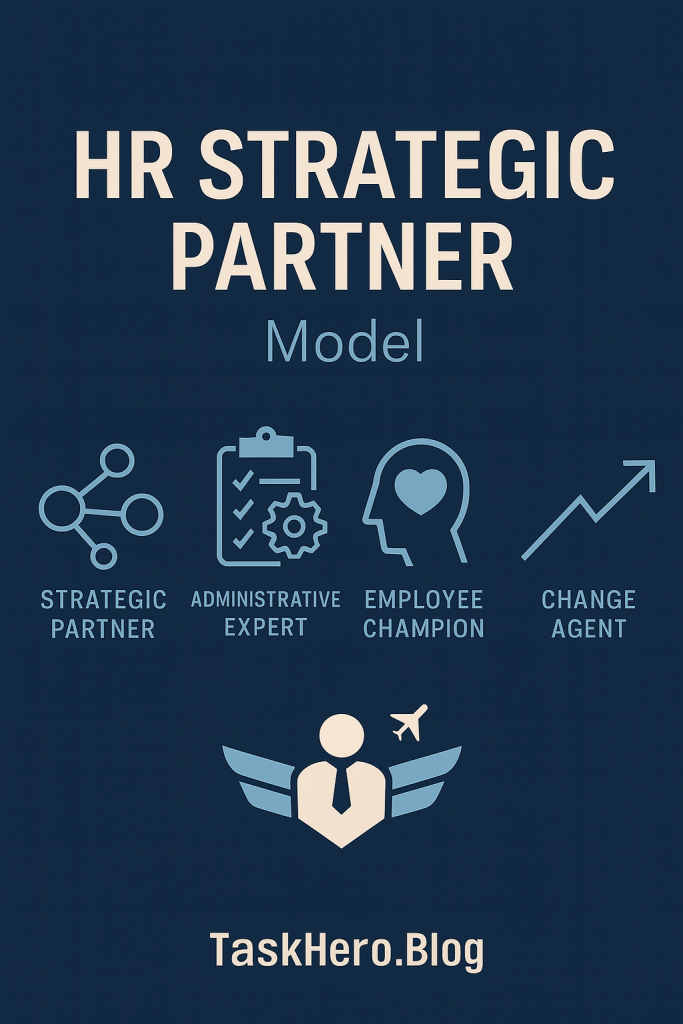
The Four Original Roles:
- Strategic Partner: Aligns HR practices with business strategy and helps drive organizational performance.
- Administrative Expert: Improves HR systems and processes for greater efficiency and consistency.
- Employee Champion: Listens to employee needs, builds morale, and strengthens engagement.
- Change Agent: Guides organizations through transformation and change initiatives.
Later Additions (Ulrich 2.0 and beyond):
- Credible Activist
- Talent Manager / Organizational Designer
- Culture and Change Steward
- Business Ally
- Operational Executor
Impact: Ulrich’s model shifted HR from a support function to a strategic business driver, delivering value to employees, leadership, and stakeholders.
Phase 4 (2000–Today): Digital Transformation
Modern HR leverages technology, analytics, and plays a strategic role in organizational growth. Key trends: hybrid work, DEI, wellness, and AI tools.
Core HR Domains
1. Recruitment & Talent Acquisition
From traditional job postings to ATS, LinkedIn sourcing, and candidate experience. Data-driven hiring ensures alignment with strategic needs.
2. Learning & Development (L&D)
Ongoing employee education through onboarding, upskilling, e-learning, leadership training, and succession planning.
3. Performance Management
Modern approaches include real-time feedback, OKRs, 360 reviews, and aligning goals with organizational outcomes.
4. Compensation & Benefits
Designing competitive pay structures, incentive systems, benefits packages. Managing payroll systems and market benchmarking.
5. Employee Relations
Managing conflict, grievances, investigations, misconduct cases, and engagement. Includes union relations where applicable.
6. Policy & Compliance
Crafting fair workplace policies, ensuring labor law compliance (GDPR, OSHA, local laws). Preventive governance and internal equity.
7. HR Business Partnering
HRBPs work directly with business leaders to align people strategy with operations. They drive change, culture, and talent planning.
8. HR Technology & HRIS
Managing digital tools for payroll, performance, learning, and data analytics. Examples include SAP SuccessFactors, Workday, etc.
9. Emerging & Specialized Areas
- Diversity, Equity & Inclusion (DEI)
- Employee Wellness & Mental Health
- People Analytics & Workforce Planning
- Organizational Development & Change Management
Conclusion
Modern HR is a strategic partner – shaping culture, optimizing talent, driving engagement, and managing change. It’s no longer about admin, but about enabling business through people.

Leave a comment